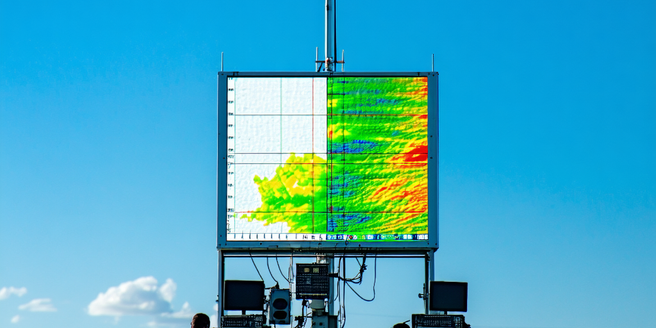
Understanding Doppler Radar Technology
Doppler radar technology is a cornerstone of modern meteorology, leveraging the Doppler effect to measure the velocity of objects at a distance. Developed to enhance the accuracy of weather forecasting, Doppler radar sends out pulses of radio waves, which bounce off particles such as raindrops or hailstones. By analyzing the frequency shift of the returned signals, meteorologists can determine not just the location of precipitation, but its motion relative to the radar itself. This capability is essential in assessing storm dynamics, such as rotation or wind shear, allowing for timely and precise weather warnings. Its utilization in tracking severe weather conditions enhances the emergency response, safeguarding communities from potential hazards before they unfold. With continued advancements, Doppler radar remains integral to understanding and predicting atmospheric phenomena.
The Evolution of Radar in Meteorology
Radar technology has undergone significant advancements since its initial development during World War II. Initially, radar’s primary function was detecting enemy aircraft, but it quickly became an invaluable tool for meteorologists. The adaptation of radar for weather monitoring led to the creation of weather radar systems capable of detecting precipitation. Throughout the decades, enhancements in radar resolution and accuracy have drastically improved our ability to observe atmospheric conditions. With the invention of Doppler radar, meteorologists gained the ability to not only identify precipitation but also measure the speed and direction of raindrops, leading to better storm tracking and forecasting. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of dual-polarization and phased array radar systems further augments weather observation capabilities, providing clearer and more detailed data essential for accurate weather prediction.
How Doppler Radar Tracks Storm Movement
Doppler radar is a vital tool for tracking storm movement, providing meteorologists with real-time data about atmospheric conditions. By capitalizing on the Doppler effect, this radar system measures changes in the frequency of radar waves reflected from precipitation particles. This data offers critical insights into wind patterns within storm systems, revealing details on their speed and movement direction. Such information is crucial for identifying rotation in supercell thunderstorms, which can indicate the potential for tornado development. Furthermore, Doppler radar aids in monitoring the intensity and evolution of storm systems, offering timely data that is essential for issuing weather alerts. By understanding storm dynamics through Doppler radar, meteorologists can provide the public with more accurate warnings, reducing the risks associated with severe weather events and ultimately saving lives.
Case Studies: Effective Storm Prediction
Effective storm prediction is showcased in various case studies where Doppler radar played a pivotal role. One notable instance is the 2011 Joplin tornado, where the timely issuance of a tornado warning, based on Doppler radar data, prompted emergency measures that undoubtedly saved lives. Detailed storm tracking allowed meteorologists to assess the tornado’s intensity and potential path, providing essential information for emergency responders. Another case is the use of Doppler radar during Hurricane Katrina, where it helped track the storm’s eye and anticipate landfall impacts on the Gulf Coast. These case studies demonstrate the critical value of Doppler radar in enhancing storm prediction accuracy. By enabling detailed analyses of storm structure and dynamics, Doppler radar supports emergency management efforts, facilitating proactive strategies to mitigate the adverse effects of severe weather events.
Future Innovations in Weather Radar Systems
As technology advances, the future of weather radar systems looks promising with innovative developments on the horizon. One such advancement is the integration of dual-polarization technology, which improves the accuracy of precipitation type identification, enhancing the ability to distinguish between rain, snow, and hail. Phased array radar is another promising innovation, offering faster data acquisition and the potential for 3D atmospheric imaging. This technology allows for more dynamic scanning of weather systems, providing a more comprehensive view. Additionally, machine learning algorithms are being integrated into radar systems, enabling more precise pattern recognition and storm prediction capabilities. These future innovations hold the promise of significantly improving weather forecasting, ultimately leading to more accurate warnings and better preparedness for weather-related challenges, safeguarding both lives and infrastructure from the adverse effects of severe weather conditions.
